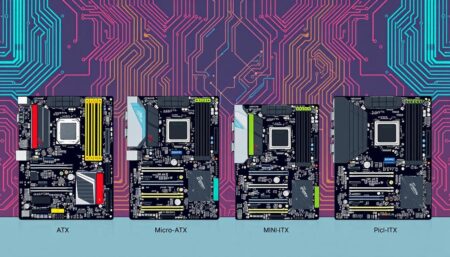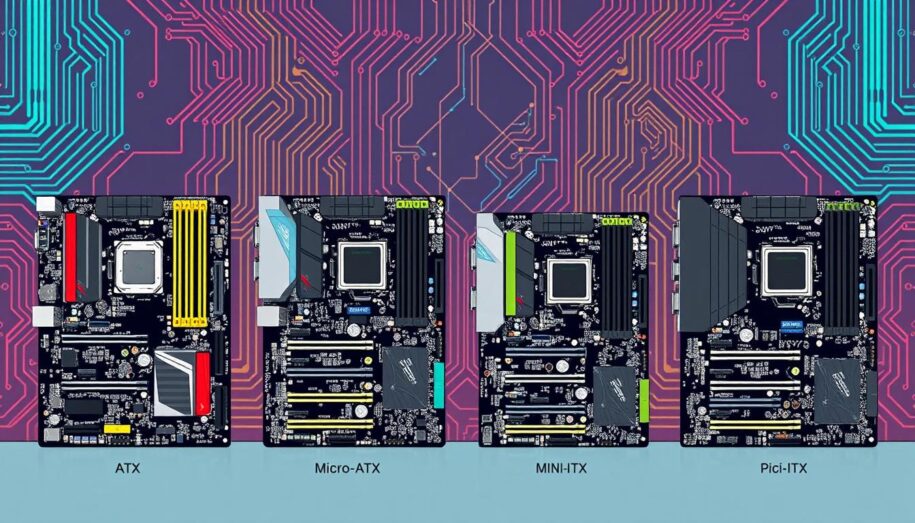
The motherboard is the heart of any computer. It affects how well your machine performs, how well it works with other parts, and how much you can add to it. Knowing about the different motherboard sizes is critical for anyone building a PC. This guide will help you understand the various sizes and their features and how to pick the best one for your needs.
A detailed illustration showcasing various motherboard sizes featuring ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX, and Pico-ITX form factors arranged side by side. Each motherboard has distinct components like CPU sockets, RAM slots, PCIe slots, and power connectors visible. The background should be a tech-themed environment with circuit patterns, highlighting the differences in size and layout of each motherboard type, all in vibrant colors and high detail.
Key Takeaways
- Motherboard form factors define the size, layout, and compatibility of critical components in a PC system.
- The correct form factor ensures proper fit, power delivery, and expansion capabilities.
- Typical form factors include ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX, and Extended ATX, each with advantages and use cases.
- Understanding different form factors’ physical dimensions, mounting points, and space requirements is essential for a successful PC build.
- Compatibility with the case, cooling solutions, and power supply are vital considerations when choosing the appropriate motherboard size.
Understanding Motherboard Form Factors: Basic Concepts
Motherboard form factors are the standard sizes and layouts of a PC’s main circuit board. They ensure the motherboard fits well with other essential parts like the computer case and power supply, which is key for a PC to work properly.
What Makes a Form Factor
A motherboard’s form factor is based on its size, mounting holes, and where ports and slots are. Groups set these rules to help computers work together smoothly.
Why Form Factors Matter
Picking the correct motherboard form factor is vital for a PC that works well. It affects how the motherboard fits in the case and where you can add more parts. The right choice means your PC will quickly set up and run well.
Standardization and Compatibility
Having standard motherboard sizes is critical for keeping things working together. It lets users mix different parts easily, making building a PC simpler. This allows you to create many different kinds of systems.
“Standardization of motherboard form factors is the foundation for a thriving PC hardware ecosystem, allowing users to build custom systems with confidence.”
Evolution of Motherboard Sizes Through History
The journey of motherboard form factors is quite interesting. It shows how technology has changed over time. From the AT form factor in the 1980s to the more recent LPX and NLX, motherboards have evolved a lot.
The AT form factor was the first standard for motherboard sizes. It was big and soon replaced by the Baby AT, which had a smaller design and was better suited for smaller systems. Then, LPX and NLX came along, each with their special features.
The BTX (Balanced Technology Extended) form factor was introduced in the early 2000s. It was a significant change from the ATX standard. BTX focused on better cooling and cable management for more efficient systems.
| Form Factor | Introduction | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| AT | 1980s | Bulky design, set initial standards |
| Baby AT | 1980s | Compact solution, space-saving |
| LPX | 1990s | Low-profile design, improved cable management |
| NLX | 1990s | Narrow design, targeted for small form factor PCs |
| BTX | Improved thermal management, an alternative to ATX | Improved thermal management, alternative to ATX |
These changes have not just made motherboards smaller. They’ve also changed how systems are designed and how they work. As technology keeps getting better, the world of motherboards is always changing.https://www.youtube.com/embed/KEAE4MtgU6s
ATX: The Modern Standard
The Advanced Technology eXtended (ATX) has become the top choice for personal computers. It was introduced in the mid-1990s. The Intel ATX specification is now the most popular for desktop systems.
ATX Power Supply Requirements
The ATX standard has precise power supply needs. It works well with standard ATX power supplies, making building and upgrading PCs easier.
Mounting and Case Compatibility
The ATX form factor makes mounting the motherboard simple. It fits in many cases, making system builds versatile.
Component Layout Benefits
The ATX standard also improves component layout. It places components like the CPU and memory slots for better cooling. This helps with airflow and system performance.
The ATX form factor is now the top choice for desktop PCs. It offers excellent power supply integration, mounting, and component layout, and it’s the modern standard in the industry.
Micro-ATX: Compact Yet Capable
The Micro-ATX (mATX) is a small but powerful motherboard choice. It’s smaller than the ATX standard but still packs a lot of punch, making it perfect for budget-friendly and space-saving builds.
The mATX is about 9.6 inches by 9.6 inches. Its small size makes it great for building high-performance systems in tight spaces. It fits nicely in ATX cases, offering flexibility in system design.
One big plus of mATX is its affordability. You can find budget-friendly mATX motherboards that still offer excellent performance. They support the latest processors and memory without the high cost of ATX setups.
| Motherboard Form Factor | Dimensions (inches) | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|
| Micro-ATX (mATX) | 9.6 x 9.6 | ATX cases |
While mATX is excellent for saving space, it might have fewer expansion slots than ATX. It’s not ideal for top-tier gaming or workstation systems. But for most users, it’s a perfect mix of size, performance, and price.
A detailed micro-ATX motherboard on a clean, sleek workbench, showcasing various components like RAM slots, CPU socket, and PCIe slots, with modern cooling solutions and RGB lighting, surrounded by tools and cables, in a bright, well-lit environment.
Common Motherboard Form Factors and Their Dimensions
Knowing about motherboard sizes is critical when building or upgrading a computer. This knowledge ensures your parts fit well and your PC case looks promising. Let’s look at the standard sizes and what makes them unique.
Standard Measurements
The most known motherboard sizes and their dimensions are:
- ATX: 12 x 9.6 inches (304.8 x 243.84 mm)
- Micro-ATX: 9.6 x 9.6 inches (243.84 x 243.84 mm)
- Mini-ITX: 6.7 x 6.7 inches (170.18 x 170.18 mm)
- Extended ATX (E-ATX): 12 x 13 inches (304.8 x 330.2 mm)
Mounting Points
The number and location of mounting holes are essential for a secure fit. Each size has its hole setup to fit its size and layout.
Space Requirements
The motherboard’s size affects case compatibility and space for other parts. Bigger sizes like ATX and E-ATX give more room for parts and cooling. Smaller sizes, like Mini-ITX, focus on being compact.
Knowing the motherboard sizes chart helps you choose the correct motherboard for your build’s needs and space.
Mini-ITX: Small Form Factor Computing
In the world of small computers, Mini-ITX stands out. It’s a top pick for SFF PC and HTPC fans. This tiny motherboard is big on power, size, and flexibility.
The Mini-ITX motherboard is only 6.7 x 6.7 inches (17 x 17 cm). It’s a small wonder that lets you build compact builds without sacrificing essential features. It can handle strong processors and graphics cards, making it great for those who want power in a small package.
Mini-ITX is perfect for home theater PC (HTPC) builds. Its small size and low profile fit well in living rooms. It’s a great media hub that doesn’t take up too much space.
| Motherboard Form Factor | Dimensions | Expansion Slots | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mini-ITX | 6.7 x 6.7 inches (17 x 17 cm) | 1-2 PCI/PCIe slots | SFF PC, HTPC, portable computers |
While Mini-ITX is super small, it has some downsides. It has fewer slots for adding parts, like graphics cards or fast storage. But, many people find its small size worth it.
Mini-ITX is an excellent choice for building compact, high-performance systems. It’s perfect for HTPC, SFF PC, or portable computers. Its size, power, and flexibility make it a standout option.
“Highly detailed Mini-ITX motherboard showcasing compact design, intricate circuitry, vibrant color components, and cooling solutions, set against a sleek, modern workspace background.”
Extended ATX (E-ATX) for High-End Systems
The Extended ATX (E-ATX) motherboard is a top pick for high-performance systems. Pros and enthusiasts favored it for its ability to handle high-end motherboards. The E-ATX standard is excellent for workstations, multi-GPU setups, and professional workstations.
Workstation Benefits
The E-ATX form factor is more significant, which means better power delivery and more slots. It’s perfect for demanding tasks like 3D rendering and video editing, and its design also supports complex cooling needs.
Gaming Applications
For those building gaming rigs with multi-GPU setups, E-ATX is the go-to. It offers extra space and slots for powerful graphics cards. This boosts gaming performance and advanced rendering tasks.
Server Capabilities
E-ATX stands out for supporting many storage options and network connections in servers. It’s also great for redundant power supplies, making it ideal for building reliable server systems that handle heavy loads well.
The Extended ATX form factor is a versatile, robust option for high-end systems. It’s perfect for workstations, gaming rigs, or servers. Its enhanced features and flexibility make it a top choice for those who want the best from their hardware.
Choosing the Right Form Factor for Your Build
Choosing the correct motherboard form factor is critical when building a custom PC. Each size has its benefits, from Mini-ITX to E-ATX. Choosing the right one can significantly impact your system’s performance and compatibility.
Consider your use, space, budget, and system needs when picking a form factor. For a primary PC or a budget build, Micro-ATX or Mini-ITX might be best. They’re small but still have all the essential features. For a top-notch gaming rig or workstation, ATX or E-ATX is better. They offer more room for upgrades, better power, and cooling.
| Form Factor | Ideal Use Case | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Mini-ITX | Space-constrained environments, basic productivity tasks | Limited expansion options, smaller component selection |
| Micro-ATX | Balanced performance and versatility, moderate space | Fewer expansion slots than ATX, less complex cooling requirements |
| ATX | Mainstream PC building, gaming, and workstation use | Widely supported, ample expansion options, cooling requirements |
| E-ATX | High-end gaming, workstations, and server applications | Larger case size requirement, specialized component selection |
You can pick the best form factor by thinking about your PC building guide, motherboard selection, and system needs. This choice will make your custom PC look great and work well, meeting your performance and functionality goals.
“Selecting the right motherboard form factor is the foundation of a successful PC build, tailoring your system to your specific needs and preferences.”
Installation and Compatibility Considerations
Building a PC requires careful planning and attention to detail. Choosing the proper PC case is essential to ensuring good airflow and power delivery. These steps can make a big difference in your build’s success.
Case Selection Guidelines
Choosing the proper PC case is critical. You must consider PC case compatibility, size, and front panel connectivity. A good case should have enough space and the correct mounting points for easy installation.
Cooling Requirements
Good airflow optimization is vital for keeping your system cool. Consider how much cooling your CPU and GPU need. The right case fans can help keep your system stable and running long.
Power Delivery Needs
Choosing the correct PSU (Power Supply Unit) is crucial. Ensure it fits your motherboard and can handle your system’s power needs. A good power supply is essential for reliable system operation.
| Consideration | Importance | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| PC Case Compatibility | High | Motherboard form factor, mounting points, dimensions |
| Airflow Optimization | High | Component heat dissipation, fan placement, ventilation |
| Power Supply Selection | High | Wattage, connectors, form factor compatibility |
Focusing on these key factors can help you build a PC that works well and meets your needs. It’s all about careful planning and attention to detail.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct motherboard form factor is critical to building a fabulous computer. From ATX to Mini-ITX, each has its benefits and meets different user needs.
Are you building a gaming rig, media center, or server? Knowing about motherboard form factors is vital. It helps you pick the best hardware for your system, ensuring top performance and compatibility with your case and other parts.
As tech advances, so will motherboard form factors. Keeping up with new designs helps you make better choices for your PC building projects. Remember, the motherboard form factor is the base of your system. Choose well and enjoy creating the perfect hardware selection for you.
FAQ
What are the most common motherboard form factors?
The most common motherboard types are ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX, and Extended ATX (E-ATX). They differ in size and layout. This affects how they fit in PC cases and use power supplies.
How do I choose the correct motherboard form factor for my PC build?
Think about your PC’s purpose and the space you have. Consider your budget and the components you’ll use. ATX and Micro-ATX are versatile. Mini-ITX and E-ATX are for more minor or high-performance builds.
What are the critical differences between ATX and Micro-ATX form factors?
ATX boards are more prominent and have more slots for components. Micro-ATX boards are smaller but still offer good features and expandability.
How do I ensure that my motherboard and PC case are compatible?
Make sure the motherboard size fits your case. Check the case’s specs for supported sizes. Ensure the motherboard’s dimensions match the case’s layout for a secure fit.
What are the power supply requirements for different motherboard form factors?
Power supply needs vary by motherboard size. ATX and E-ATX need standard ATX supplies. Micro-ATX and Mini-ITX might use smaller supplies. Always check the motherboard’s specs for the correct supply size and connectors.
How do I ensure proper cooling for my motherboard and components?
Good cooling is vital for your PC’s stability and life. Choose a motherboard that fits your case’s airflow. Ensure your CPU cooler and fans match your motherboard’s size and layout.